 |
 |
 |
| |
| Environment/objects of interest |
- Nahe Valley
- Soonwald
- Idarwald
- Hochwald
- Mosel Valley
- Rhein Valley
- Districts
The romantic Nahe valley
 The headwaters of the Nahe river lie in a forest valley, 460 m above sea level, above the village of Selbach in the Saarland district of St. Wendel. The constantly changing landscape with its extensive forests, narrow ravines, and wide floodplains that abruptly open up, follow the river on its 112 km route to the Rhine. On the upper Nahe, in the Idar-Oberstein area, one finds semi-precious stones such as agates, amethysts, mountain crystals and chalcedony, which were commercially mined until the end of the 19th Century. In Kirn, the next largest small town, there is a splendid view from the ruins of Kyrburg. A little downstream from Bad Sobernheim , at the foot of Disibodenberg , the largest tributary, the
water-rich Glan, flows into the Nahe. In the Glan valley lies Meisenheim , with an old town from the Middle Ages which is worth seeing. From Disibodenberg, the Nahe flows onwards to Bad Münster am Stein and Bad Kreuznach, where saltwater springs are the basis for the health and spa industry. In the past, these saltwater springs also served as sources for salt (salt works and graduation houses). A few kilometers northwest of Bad Kreuznach, in the Ellerbach valley, lies Sponheim with the former monastery church of St. Martin, the most significant romanesque building in the Nahe-Hunsrück region. Near Bingen the Nahe finally reaches the Rhine.
Above is a picture from Lemberg, which is near Bad Münster am Stein in the middle of a 100,000 hectare nature preserve with steep mountain slopes covered by enormous amounts of scree and many rare plants. From the peak of Lemberg one has an unparalleled view of the Nahe Valley below as well as over a wide part of Hunsrück. A picture book worth seeing: Naheland Impressionen; Kreisverwaltung Bad Kreuznach, 1994 The headwaters of the Nahe river lie in a forest valley, 460 m above sea level, above the village of Selbach in the Saarland district of St. Wendel. The constantly changing landscape with its extensive forests, narrow ravines, and wide floodplains that abruptly open up, follow the river on its 112 km route to the Rhine. On the upper Nahe, in the Idar-Oberstein area, one finds semi-precious stones such as agates, amethysts, mountain crystals and chalcedony, which were commercially mined until the end of the 19th Century. In Kirn, the next largest small town, there is a splendid view from the ruins of Kyrburg. A little downstream from Bad Sobernheim , at the foot of Disibodenberg , the largest tributary, the
water-rich Glan, flows into the Nahe. In the Glan valley lies Meisenheim , with an old town from the Middle Ages which is worth seeing. From Disibodenberg, the Nahe flows onwards to Bad Münster am Stein and Bad Kreuznach, where saltwater springs are the basis for the health and spa industry. In the past, these saltwater springs also served as sources for salt (salt works and graduation houses). A few kilometers northwest of Bad Kreuznach, in the Ellerbach valley, lies Sponheim with the former monastery church of St. Martin, the most significant romanesque building in the Nahe-Hunsrück region. Near Bingen the Nahe finally reaches the Rhine.
Above is a picture from Lemberg, which is near Bad Münster am Stein in the middle of a 100,000 hectare nature preserve with steep mountain slopes covered by enormous amounts of scree and many rare plants. From the peak of Lemberg one has an unparalleled view of the Nahe Valley below as well as over a wide part of Hunsrück. A picture book worth seeing: Naheland Impressionen; Kreisverwaltung Bad Kreuznach, 1994 |
Soonwald
The Soonwald is one of the largest contiguous areas of forest in Germany. Its altitude (400-600 m; the highest peak is Ellerspring at 657 m), its low population density, and its distance from the large transportation routes of our time make it an ideal recreation area for people seeking peace and quiet. This wooded area is well developed. It has over 800 km of circular hiking paths with observation towers at the most beautiful spots, which afford spectacular panoramas. You can hike here for hours without ever meeting another human being, although traces of more than two thousand years of human history can be found everywhere. There are, on the heights of mountain ridges, ancient Celtic hilltop forts, surrounded by gigantic stone walls which easily exceed several hundred meters in length; there are ancient Roman long-distance roads, constructed some 2,000 years ago at a standardized width of 5 to 6 meters and protected by watchtowers at regular
intervals; and there are the remains of luxurious Roman villas. In addition, we find medieval fortresses and castles from the glory days of the political might of Sponheim and Kurtrier. And, there are churches and monasteries in the architectural style typical of Hunsrück with ingeniously painted surfaces and galleries; evidence of a very special race of people, who despite difficult living conditions and scant resources created their own works of art over hundreds of years. A race of people who, incidentally, you still encounter today on the farms of the elevated plains or in the village guest houses.
A picture book worth looking at: Uwe Anhäuser, Kultur-Erlebnis Hunsrück; Idar-Oberstein: Dr. Gebhardt & Hilden, 2000
Wanderführer: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000
Ergänzende Literatur: Landesgeschichtlicher Exkursionsführer Hunsrück; mit Beiträgen von A. Bauer, B. Lipps, W.H. München, E. Schaaf und K.H. Weichert, Herausgeber: Hunsrückverein e.V., Arbogast Verlag Otterbach, 1993 |
Wildenburg Mountain near Kempfeld 
On the top of Wildenburg Mountain (Wildenburger Kopf), one of the highest peaks of Wildenburg Ridge at 675 m, stood an important Celtic refuge with a double ring wall during the Latène Age (500 to 20 BC). Together with the grounds further west near Otzenhausen and on Ringskopf mountain, as well as the "Altburg" fortress further east near Bundenbach, this formed an extensive system for defense and protection by the Celtic tribe of Treverians. The key strategic importance of Wildenburg for those times becomes clear when you stand on the platform of the observation tower and enjoy the sweeping panoramic views —an extremely rewarding outing at any time of year and in any weather. To the north you can see the Eifel region and to the Ardennes, to the east the Taunus region,
and in the southeast you recognize the prominent massif of Donnersberg mountain. At 687m, Donnersberg is the highest point of the Nordpfalz Region, on whose summit plateau rests the third largest Celtic "oppidum" of central Europe, with an 8.5km long system of ring walls and an enclosed area of 240 hectares. By contrast, with an interior area of 6 hectares, the dimensions of the Wildenburg refuge (with the largest dimensions 300 m by 220 m) were quite modest, yet for the Hunsrück region it represented a characteristic size for Celtic castles. In fact, the economic and social system of the Celts of the Latène Age developed into an early urban form of society due to the prosperous economy; the so-called Oppida Civilization. Characteristic of this civilization at the time of Caesar was a form of settlement which primarily consisted of individual farmsteads (Latin: aedificia), unfortified villages (Latin: vici), and fortified towns
(Latin: oppida).
After Ceasar conquered the Galls (58-51 BC) and subjugated the Celtic tribe of Treverians, a Roman mountain temple arose on the top of Wildenburg. It is unclear whether the Celtic castle was still being used at the time of the Roman conquest. Around the year 350 AD a Late Roman fortification was constructed on Wildenburg for a short time. Wildenburg gets its name from the Wildgrave Friedrich von Kyrburg from Kirn on the Nahe River, nobleman of the status of count, who, in the year 1328, built a small castle on an exposed spur on the top of Wildenburg Mountain. In the process, a substantial part of the Celtic ring walls were used, and thereby destroyed, as a stone quarry. Due to its exposed position, the only easy approach to the castle was on the heights of the mountain ridge, so that two man-made moats were enough to secure it, hewn into the rock at a 10 m distance to each other and still visible today. With these moats, a wooden bridge
was the only way to reach the castle, which was burned down by Lorraine troops in the year 1651. Later it was partially reconstructed, and in the year 1660 the lower part of the castle served the bailiwick of Wildenburg as administrative seat until the county was abolished in the year 1792.
Today a 22 m high observation tower, which was erected by the Hunsrück Society (association for the advancement of cultural heritage), stands on the rocky spur on top of Wildenburg mountain. At the foot of the castle hill, on the medieval foundation wall of the castle's lower part, a rustic-style restaurant has arisen. An "historic" learning trail leads through the more than three thousand years of human history, which is all around. In addition, a newly established "forest adventure trail" will enthrall adults and children alike. This 3.5 km long circular path through the woods around Wildenburg allows you to see in reality how a forest rejuvenates naturally, which characteristics can be used to identify trees, where the wild animals are, how people used to make charcoal, and many more interesting facts. |
Hochwald with the Erbeskopf (818 m) 
The Hochwald with its dense forests surrounding the 818 meter high Erbeskopf (the highest mountain west of the Rhine in Germany) is a fertile source of sagas and heroic tales. Many researchers of local history suspect that here in this pristine area of the Hunsrück plays one of the central scenes of the medieval Nibelungenlied.
In this place, according to the saga, Hagen von Tronje slew the noble hero Siegfried at the behest of Brunhilde. In fact, Drohnecken castle at the foot of Erbeskopf mountain is thought to be a possible family seat of Hagen von Tronje. Hagen's friend Hunold is thought to come from the nearby Hunolstein castle. Moreover, the towns of Worms and Alzey —the most important locations in the Nibelungenlied— are little more than a day ride on horseback from the Hunsrück mountain range.
A picture book worth looking at: Uwe Anhäuser, Heimat am Idarwald; VG Rhaunen, 2001
Hiking Guides: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000 |
The Mosel valley from Trier to Koblenz 
The Mosel river with its length of 545km, isn't even half as long as the Rhine. It has its source in the southern Vosges, from where it winds through the area of Trier in order to reach a branch of the Hunsrück.
From there, until it meets the Rhine at Koblenz, it flows through the deeply cut, winding valleys of the Rhenish slate mountains, creating a natural boundary at the north of the Hunsrück. The Mosel valley is an important wine growing area with famous names such as Bernkastel, Traben-Trarbach, Zell and Cochem.
Guide book: Reinhold Schommers, Mosel; DuMont Buchverlag, 2001 |
The Rhine valley from Bingen to Koblenz
The Rhine has covered two thirds of its 1320 km long trip from the Swiss Alps (canton Graubünden) to the North Sea by the time it meets a branch of the Hunsrück near Bingen. Starting here, it flows through the slate mountains of the middle Rhine region. The traveler passes through a very narrow 300m deep ravine where the Hunsrück is a natural boundary. Then he traverses the fascinating landscape of Hunsrück on his way downstream.
Along this way he sees world famous places such as Bacharach, Kaub, or St. Goar with the overwhelming rock of Loreley. He sees Boppard with its impressive Rhine loop and picturesque Rhens. At Koblenz, at the mouth of the Mosel in the Rhine, he has reached the most northerly point of the branch of the Hunsrück. It isn't far from here and the Rhine widens, with all the narrows left behind. The low plains now determine the flow of the Rhine to the North Sea.
Hiking guide: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000 |
Three districts, one region: Nahetal-Hunsrück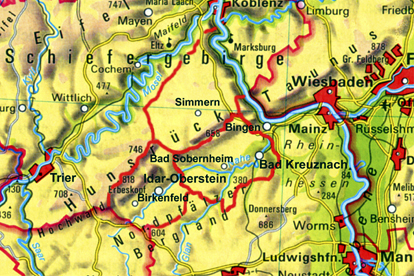
The region of the Nahe Valley-Hunsrück, the historic Nahegau, is divided into three administrative districts: to the east lies the district of Bad Kreuznach with its administrative seat in the city of Bad Kreuznach, to the north is the district of Rhein-Hunsrück with its administrative seat in Simmern, and to the west is the district of Birkenfeld with its administrative seat in the city of Birkenfeld. To the north there are also the districts of Cochem-Zell and Bernkastel-Wittlich bordering the Mosel river. Although the form these districts have today only dates from the administrative reform of the Rhineland-Pfalz region in 1969/1970, their origins can be found 200 years earlier. First under the French ruler Napoleon and then, after the reconstruction of Europe by the Viennese congress, under the Kingdom of Prussia. In fact, in the year 1798, under French
rule (1798-1814), the feudal system with its class privilege, serfdom and drudgery was eliminated, and, to ensure the division of authority, administrative and judicial powers were separated. All religious faiths received equal rights, and in 1804 these rights were implemented by a unified code of law, the Napoleonic civil code (Code civile Napoléon). As a result of an act of the Viennese Congress, the final act of 9 June 1815, the Prussians were awarded the area north of the Nahe. On 14 May 1816, the "royal government" in Koblenz officially announced the newly formed "districts" as administrative units, so this date is considered the official "birthday" of these districts.
It should be mentioned that the historical "Nahegau" only encompassed the eastern part of the District of Birkenfeld. The border ran along the Heimbach, a few kilometers west of Baumholder, along the Nahe up to Siesbach, just before Idar-Oberstein, along the Siesbach almost to the Erbeskopf, and from there over the ridge of the Idar forest to the Idarkopf. A look at the map here also shows that the mouth of the Nahe near Bingen (belonging to the district of Mainz-Bingen) and the northwestern part of Hunsrück (belonging to the districts of Cochem-Zell and Bernkastel-Wittlich) complete the region.
Along with the federal and state duties dictated, the district administration is also responsible for schools, social welfare, youth welfare offices, building development, land utilization, and fire protection. In addition, it deals with waste management as well as the maintenance of local streets. Above and beyond these central administrative tasks, the district also provides for the economic development of the community and region. In this respect, the expression "sustainability", as well as sustainable development, plays a central role, since its professed goal is to ensure the "continuance of a balance in the relationship between nature and its ability to regenerate, on the one hand, with its claims by humans, on the other". Alongside its obligatory duties, the district also takes on so-called "voluntary" duties, depending upon the tax income. Among these are the maintenance of adult evening classes, music
schools, museums, theaters, sports fields, and swimming pools.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Hotel Maasberg Therme • 55566 Bad Sobernheim • Tel: + 49 (0 67 51) 87 60 • Fax: + 49 (0 67 51) 87 62 01 • E-mail: info@maasberg-therme.de |

