 |
 |
 |
| |
| Environment/objects of interest |
- Nahe Valley
- Soonwald
- Idarwald
- Hochwald
- Mosel Valley
- Rhein Valley
- Districts
Geology of the Nahe valley 
400 million years ago, in the Devonian period, Europe was near the equator, and the climate was warm. A shallow ocean with islands covered central Europe. Hunsrück was a deeper basin of this ocean with a stable layering of water. The upper water layers were rich in oxygen and supportive to life, whereas the lower levels were poor in oxygen and poisoned by hydrogen sulfide. The remains of living organisms sank into the black mud and were quickly conserved by ferrous sulphide. This is the reason they are so well conserved. In the slate quarry near Bundenbach numerous renowned fossils were found that, when x-rayed, showed even the finest details. The rivers that flowed into the Devonian sea deposited large amounts of muddy sediments, sand, gravel and clay which, through heat and pressure during millions of years, became layers of stone and rock. In this way, and depending upon material
and coarseness slate, sandstone, and with a high percentage of quartz grains, Taunus quartzite were created.
300 million years ago, at the end of the Carboniferous period, the Devonian layers of the Hunsrück were pushed together by massive pressure from southeast to northwest creating the northern chain of the Variszicum mountains. Together with the Hochwald, Idarwald, and Soonwald chains, a high mountain range was formed. The debris resulting from erosion and weathering of this range was deposited in the basin on the south flank, building up the "Unterrotliegende". After another rising of the mountains and sinking of the basin the process was repeated, creating the "Oberrotliegende". In the Permian period the creation of mountains was accompanied by strong volcanic activity on the southern fault of the Hunsrück. Lava springing forth from inside the earth cooled and formed harder layers than the Rotliegende. Depending upon the composition of the lava and the rate of cooling,
very different types of rock were created: From thin lava with little silicic acid (SiO2), came Basalt, Melaphyre and Dolerite (Hellberg), lava with a medium level of SiO2, created Andesite and Porphyre (Lemberg) and from thick lava with a high level of SiO2, red colored Rhyolite (Rotenfels). Occasionally gas bubbles were conserved in the lava and later filled with minerals forming Agate geodes. This combination of geological formations weathering at different rates, is the basis for the varied landscape of the Nahe valley. There are rocky narrows where the river must force itself through, and wide valley meadowlands where debris could be washed away more easily. The illustration above shows the Rotenfels massif, the highest cliff wall on this side of the alps and a popular destination for climbers.
The landscape of the lower Nahe between Bad Sobernheim, Bad Kreuznach and Bingen still essentially resembles how it was 35 million years ago in the Oligocene period. At that time, the valley was covered by an ocean. The coasts of this ocean ran along the bay of Kreuznach and the bay of Staudernheim (Bad Sobernheim), with an archipelago of islands in the south. It is a great exception in the history of the earth, that the coastlines of earlier epochs have been conserved. In the bay of Kreuznach, one can literally touch the areas of mainland, beach and sea bottom of the Oligocene even after 35 million years. In the sand pits, one can find petrified pine cones, which have been conserved in the beach sand ("stony peas") or admire the sea cliff south of Bad Kreuznach upon the Steigerberg, an island of the Oligocene sea.
Short Glossary of geological terminology. |
Soonwald
The Soonwald is one of the largest contiguous areas of forest in Germany. Its altitude (400-600 m; the highest peak is Ellerspring at 657 m), its low population density, and its distance from the large transportation routes of our time make it an ideal recreation area for people seeking peace and quiet. This wooded area is well developed. It has over 800 km of circular hiking paths with observation towers at the most beautiful spots, which afford spectacular panoramas. You can hike here for hours without ever meeting another human being, although traces of more than two thousand years of human history can be found everywhere. There are, on the heights of mountain ridges, ancient Celtic hilltop forts, surrounded by gigantic stone walls which easily exceed several hundred meters in length; there are ancient Roman long-distance roads, constructed some 2,000 years ago at a standardized width of 5 to 6 meters and protected by watchtowers at regular
intervals; and there are the remains of luxurious Roman villas. In addition, we find medieval fortresses and castles from the glory days of the political might of Sponheim and Kurtrier. And, there are churches and monasteries in the architectural style typical of Hunsrück with ingeniously painted surfaces and galleries; evidence of a very special race of people, who despite difficult living conditions and scant resources created their own works of art over hundreds of years. A race of people who, incidentally, you still encounter today on the farms of the elevated plains or in the village guest houses.
A picture book worth looking at: Uwe Anhäuser, Kultur-Erlebnis Hunsrück; Idar-Oberstein: Dr. Gebhardt & Hilden, 2000
Wanderführer: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000
Ergänzende Literatur: Landesgeschichtlicher Exkursionsführer Hunsrück; mit Beiträgen von A. Bauer, B. Lipps, W.H. München, E. Schaaf und K.H. Weichert, Herausgeber: Hunsrückverein e.V., Arbogast Verlag Otterbach, 1993 |
Idarwald mit Idarkopf (746 m) 
Lonely forests, peaceful creek valleys, and protected moors are the distinguishing features of Idarwald mountain range, a quartzite ridge whose two highest points are An den zwei Steinen (766 m) and Idarkopf (746 m). It is not only the extensive stretches of untouched nature that fascinates visitors and draws them from near and far. The "German Gem Road" from Idar-Oberstein leads through such picturesque places as Herrstein, Schauren, and Allenbach into the heart of the region. Relaxation, enjoyment of nature and the landscape, looking for minerals, and getting enthusiastic about the manufacture and processing of gemstones —all this can be combined here in the most pleasant way. What should also not be overlooked are distinct traces of a very old cultural landscape, whose roots reach far back into prehistoric times, which can be found everywhere. The reconstructed Celtic 'Altburg' fortress near Bundenbach or the 'Belginum' archaeological
park near Morbach allow you to experience this era up close. The only castle surrounded by water in Hunsrück is located near Morbach and reminds us of the Trier Archbishop and Elector Balduin von Luxemburg, one of the greatest protagonists of the Middle Ages in Hunsrück.
A picture book worth looking at: Uwe Anhäuser, Heimat am Idarwald; VG Rhaunen, 2001
Hiking guides: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000 |
Hochwald with the Erbeskopf (818 m) 
The Hochwald with its dense forests surrounding the 818 meter high Erbeskopf (the highest mountain west of the Rhine in Germany) is a fertile source of sagas and heroic tales. Many researchers of local history suspect that here in this pristine area of the Hunsrück plays one of the central scenes of the medieval Nibelungenlied.
In this place, according to the saga, Hagen von Tronje slew the noble hero Siegfried at the behest of Brunhilde. In fact, Drohnecken castle at the foot of Erbeskopf mountain is thought to be a possible family seat of Hagen von Tronje. Hagen's friend Hunold is thought to come from the nearby Hunolstein castle. Moreover, the towns of Worms and Alzey —the most important locations in the Nibelungenlied— are little more than a day ride on horseback from the Hunsrück mountain range.
A picture book worth looking at: Uwe Anhäuser, Heimat am Idarwald; VG Rhaunen, 2001
Hiking Guides: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000 |
The Mosel valley from Trier to Koblenz 
The Mosel river with its length of 545km, isn't even half as long as the Rhine. It has its source in the southern Vosges, from where it winds through the area of Trier in order to reach a branch of the Hunsrück.
From there, until it meets the Rhine at Koblenz, it flows through the deeply cut, winding valleys of the Rhenish slate mountains, creating a natural boundary at the north of the Hunsrück. The Mosel valley is an important wine growing area with famous names such as Bernkastel, Traben-Trarbach, Zell and Cochem.
Guide book: Reinhold Schommers, Mosel; DuMont Buchverlag, 2001 |
The Rhine valley from Bingen to Koblenz
The Rhine has covered two thirds of its 1320 km long trip from the Swiss Alps (canton Graubünden) to the North Sea by the time it meets a branch of the Hunsrück near Bingen. Starting here, it flows through the slate mountains of the middle Rhine region. The traveler passes through a very narrow 300m deep ravine where the Hunsrück is a natural boundary. Then he traverses the fascinating landscape of Hunsrück on his way downstream.
Along this way he sees world famous places such as Bacharach, Kaub, or St. Goar with the overwhelming rock of Loreley. He sees Boppard with its impressive Rhine loop and picturesque Rhens. At Koblenz, at the mouth of the Mosel in the Rhine, he has reached the most northerly point of the branch of the Hunsrück. It isn't far from here and the Rhine widens, with all the narrows left behind. The low plains now determine the flow of the Rhine to the North Sea.
Hiking guide: Wolfgang Bartels, Hunsrück; DuMont Buchverlag, 1996 und Norbert Forsch, Hunsrück; Deutscher Wanderverlag, 2000 |
Three districts, one region: Nahetal-Hunsrück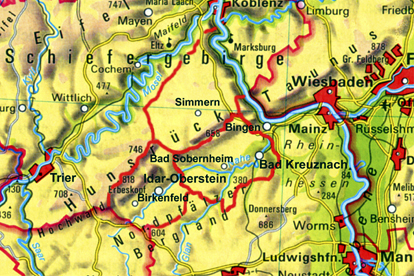
The region of the Nahe Valley-Hunsrück, the historic Nahegau, is divided into three administrative districts: to the east lies the district of Bad Kreuznach with its administrative seat in the city of Bad Kreuznach, to the north is the district of Rhein-Hunsrück with its administrative seat in Simmern, and to the west is the district of Birkenfeld with its administrative seat in the city of Birkenfeld. To the north there are also the districts of Cochem-Zell and Bernkastel-Wittlich bordering the Mosel river. Although the form these districts have today only dates from the administrative reform of the Rhineland-Pfalz region in 1969/1970, their origins can be found 200 years earlier. First under the French ruler Napoleon and then, after the reconstruction of Europe by the Viennese congress, under the Kingdom of Prussia. In fact, in the year 1798, under French
rule (1798-1814), the feudal system with its class privilege, serfdom and drudgery was eliminated, and, to ensure the division of authority, administrative and judicial powers were separated. All religious faiths received equal rights, and in 1804 these rights were implemented by a unified code of law, the Napoleonic civil code (Code civile Napoléon). As a result of an act of the Viennese Congress, the final act of 9 June 1815, the Prussians were awarded the area north of the Nahe. On 14 May 1816, the "royal government" in Koblenz officially announced the newly formed "districts" as administrative units, so this date is considered the official "birthday" of these districts.
It should be mentioned that the historical "Nahegau" only encompassed the eastern part of the District of Birkenfeld. The border ran along the Heimbach, a few kilometers west of Baumholder, along the Nahe up to Siesbach, just before Idar-Oberstein, along the Siesbach almost to the Erbeskopf, and from there over the ridge of the Idar forest to the Idarkopf. A look at the map here also shows that the mouth of the Nahe near Bingen (belonging to the district of Mainz-Bingen) and the northwestern part of Hunsrück (belonging to the districts of Cochem-Zell and Bernkastel-Wittlich) complete the region.
Along with the federal and state duties dictated, the district administration is also responsible for schools, social welfare, youth welfare offices, building development, land utilization, and fire protection. In addition, it deals with waste management as well as the maintenance of local streets. Above and beyond these central administrative tasks, the district also provides for the economic development of the community and region. In this respect, the expression "sustainability", as well as sustainable development, plays a central role, since its professed goal is to ensure the "continuance of a balance in the relationship between nature and its ability to regenerate, on the one hand, with its claims by humans, on the other". Alongside its obligatory duties, the district also takes on so-called "voluntary" duties, depending upon the tax income. Among these are the maintenance of adult evening classes, music
schools, museums, theaters, sports fields, and swimming pools.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Hotel Maasberg Therme • 55566 Bad Sobernheim • Tel: + 49 (0 67 51) 87 60 • Fax: + 49 (0 67 51) 87 62 01 • E-mail: info@maasberg-therme.de |

